Most homes in Canada have a heating system. It uses more energy than any other appliance in your home. If your system is more than a decade old, it may be time to consider purchasing a new heating system. Modern heating systems are much more energy-friendly than older ones.
To buy the correct furnace for your home, you must have a basic understanding of it.
Energy Source
In most parts of Canada, natural gas is available and popular. Some areas also have propane gas or LP gas. You can also have an electric heat pump. The least common fuel is fuel oil.
Remember to determine the fuel that is available in your area. You can have a contractor give you the estimated cost for operating for different fuels as you will need to know that, too.
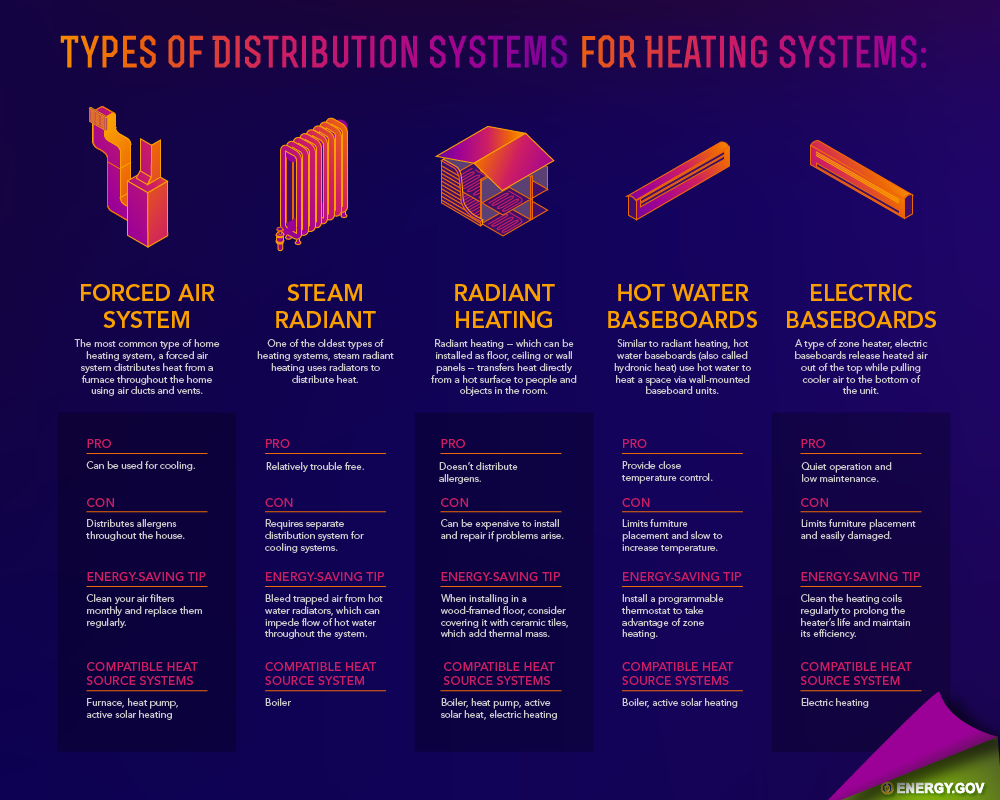
Distribution system
A heating system either warms a house with forced air or hot water. Forced-air systems blows warm air through ducts. In contrast, boilers circulate hot water by way of plastic or copper piping. In many cases, such as in my home, the hot water circulates underneath the floor. The heat from the hot pipes radiates upward throughout the house.
These systems have advantages and disadvantages. The advantage for forced-air heating is that the ducts can be used for central air conditioning. The disadvantage is that the air may seem cool since moving air will seem cooler when it moves. If you have an oversized unit, then there could also be a short burst of hot air which will cause uncomfortable temperature swings. Ductwork can not only circulate air, but also air and dust, and it can also transmit furnace noise. Your ducts can also leak which will increase your heating costs by 20-30 percent. If you prefer to have a forced-air system, make sure that the ducts are sealed properly.
The advantage of a hot water system is that it distributes even temperature and the boiler can be used for domestic hot water. The disadvantage is that the installation cost is higher. It also doesn’t allow for central air conditioning, ventilation and filtering.
If you are purchasing a new home, then it would be best to decide if you would like to have central air conditioning.
Efficiency
If the efficiency of a system is high, then the operating cost will be less.
For a residential heating system, the standard efficiency rating is AFUE or Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency. This is for systems that use natural, propane, and fuel oils. Electric heat pumps are rated by the HSPF or Heating Season Performance Factor.
These ratings measure the seasonal efficiency.
Overall cost
The initial cost is one thing to consider. However, it’s best to consider your operating cost for it entire lifespan and maintenance cost. You can refer to the yellow and black Energy Guide label for the estimate annual cost. The maintenance cost should be determined by a heating contractor.
System types:
- Furnaces: a furnace can either run on natural gas, propane gas or oil. The AFUE is around 78-96 percent. They are categorized into three:
- Base model. The AFUE is normally 78-80 percent. Better electric ignition, heat exchangers, and internal vent dampers cause the increase in the efficiency. If you are in a milder climate, then this would be the cost-effective option.
- Mid-efficiency furnace. For gas and propane the AFUE is up to 83 percent while oil can reach up to 87 percent AFUE. They a more efficient heat exchanger and the control of combustion air and the venting are more precise. They also incorporate a “high-static” burner which allows the system to extract more heat from the energy source.
- High efficiency. The AFUE is around 90-96 percent. This type uses a second heat exchanger which allows the system to take the heat that’s lost. The heat taken will be in a form of water vapor. This will then be condensed which allows the heat to be an addition in the useable heat. The condensation also allows the exhaust temperature to be lowed so it can be vented via a plastic pipe. It’s a more expensive system but is cost-effective in cold climates.
- Aside from the AFUE, you would also want to consider the electrical efficiency. The fan motor uses electricity so you will need to find a system that has high electrical efficiency. Fan motors with variable speed add to the efficiency.
- Boilers: boilers are also rated with AFUE. The AFUE of boilers that are manufactured since 1992 should be at least 80 percent. The AFUE of older units are 55-65 percent. In purchasing a new boiler, you will need to consider the controls, electrical requirements and indirect water heating ability.
Controls should be efficient to reduce the loss during the off-cycle times. Modulating aquastats reduce the operating costs. An aquastat adjusts the water temperature based on the temperature outside.
Boilers use electricity, too. This is for the circulating pumps. A new system should have high-efficiency pumps.
A new heating boiler doesn’t heat and store water simultaneously which gives efficient water heating. If have a new boiler to install, you might want to replace the existing water heater with a tank that is well insulated.
- Electric heat pumps: a heat pump uses a refrigerant cycle like an air conditioner. However, during the cold season, it can provide heat be reversing the cycle. They are more energy-efficient and the cost is comparable to that of a gas furnace. The rating for a heat pump is HSPF. The minimum is 7.6 while the high-efficient can have up to 9 HSPF or even higher. Note that high HSPF is equal to low annual heating costs.
An even more efficient heat pump is the geothermal heat pump. It absorbs heat from the ground or water that it pumped below the ground. The rating for its efficiency is called COP or Coefficient of Performance. New geothermal heat pumps can have ratings from 2.5 to 4.0. a COP of 3 is roughly the equivalent of 10 HSPF. This type can be more expensive than air source heat pumps.
A ductless or a mini-split is a new type of heat pump. In a home that doesn’t have a ductwork, then this is a great option. In each room, you can place a wall-mounted unit. These units are all connected to an outdoor unit. This type gives you heating and cooling without the need fopr a ductwork.
Sizing
Proper sizing affects the performance of a system greatly. Remember that bigger is not always better. A large unit will be able to meet your demand but will not reach its efficiency.
Before you install a unit, make sure to have your contractor perform the heating load calculation so you would be able to know the right unit that is fit your home.
Choosing a heating system can be difficult. Many are not aware of the information that are stated above which will cost them a lot of money and effort. To be able to isolate yourself from this group, it would be best to take all the information and apply it on your next purchase of a heating system.